What is the Scientific Method?
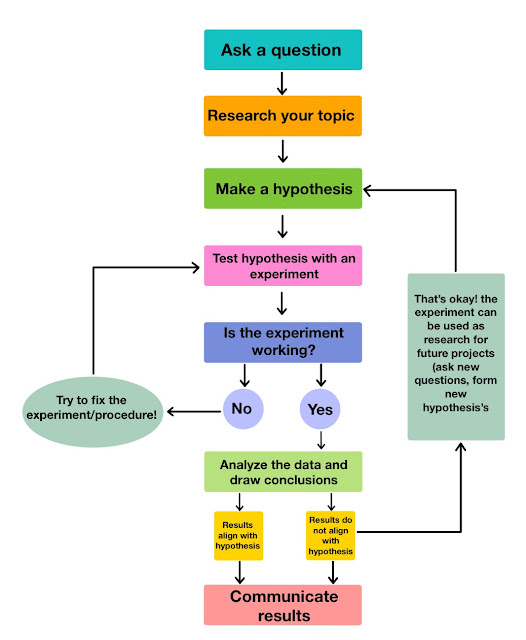
Steps of the Scientific Method
1. Ask a Question
The scientific method starts when you ask a question about something that you observe: How, What, When, Who, Which, Why, or Where?
For a science fair project, some teachers require that the question be something you can measure, preferably with a number.
2. Do Background Research
Rather than starting from scratch in putting together a plan for answering your question, you want to be a savvy scientist using library and Internet research to help you find the best way to do things and ensure that you don't repeat mistakes from the past.
3. Construct a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an educated guess about how things work. It is an attempt to answer your question with an explanation that can be tested. A good hypothesis allows you to then make a prediction:
"If _____[I do this] _____, then _____[this]_____ will happen."
State both your hypothesis and the resulting prediction you will be testing. Predictions must be easy to measure.
4. Test Your Hypothesis by Doing an Experiment
Your experiment tests whether your prediction is accurate and thus your hypothesis is supported or not. Your experiment needs to be a fair test. You conduct a fair test by making sure that you change only one factor at a time while keeping all other conditions the same.
You should also repeat your experiments several times to make sure that the first results weren't just an accident.
5. Analyze Your Data and Draw a Conclusion
Once your experiment is complete, you collect your measurements and analyze them to see if they support your hypothesis or not.
Scientists often find that their predictions were not accurate and their hypothesis was not supported, and in such cases, they will communicate the results of their experiment and then go back and construct a new hypothesis and prediction based on the information they learned during their experiment. This starts much of the process of the scientific method over again. Even if they find that their hypothesis was supported, they may want to test it again in a new way.
6. Communicate Your Results
To complete your science fair project you will communicate your results to others in a final report and/or a display board. Professional scientists do almost exactly the same thing by publishing their final report in a scientific journal or by presenting their results on a poster or during a talk at a scientific meeting. In a science fair, judges are interested in your findings regardless of whether or not they support your original hypothesis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the six steps of the scientific method?
What is a scientific method example?
- Ask a Question: Why does Greenland look so large on a map?
- Background Research: Learn that Greenland is a quarter the size of the United States in land mass. Also learn that Mercator projection maps are made by transferring the images from a sphere to a sheet of paper wrapped around the sphere in a cylinder.
- Hypothesis: If I make a Mercator projection map, then the items in the middle of the map will look their true size and the items at the poles will look larger than they really are.
- Experiment: Use a sphere with 1-inch by 1-inch squares at each pole and the equator to make a Mercator projection map. Measure the squares on the Mercator projection map.
- Analyze Data and Make Conclusions: The middle-of-the-map squares average 1 inch per side while the squares at the poles average 3 inches per side. In conclusion, the projection process used to make Mercator projection maps creates distortion at the poles, but not at the equator. This is why Greenland, which is close to the North Pole, looks larger than it is.
- Communicate: Make a video, write a report, or give a presentation to educate others about the experiment.


















0 Comments
Thank you for being here.. Tell us what you think.